At the beginning of the 21st century, one of the major problems that mankind has to face and will have to face also in the future is represented by the global warming phenomenon.
At the beginning of the 21st century, one of the major problems that mankind has to face and will have to face also in the future is represented by the global warming phenomenon.
The consequence had on globe´s flora and fauna – already a well-known subject of the written press and audio-visual media from all over the world – reached a critical stage. At the beginning of the 21st century, one of the major problems that mankind has to face and will have to face also in the future is represented by the global warming phenomenon.
The consequence had on globe´s flora and fauna – already a well-known subject of the written press and audio-visual media from all over the world – reached a critical stage.
The main cause of this phenomenon has its origin in the human community´s activities. Therefore science people launched an alarm signal letting everyone know that the ice cap melting speed reached a record level.
In 2007, the ice cap reached the lowest sizes registered in the last 30 years of satellite record. A NASA study proved that 23% of losses were registered during last winters.
“The ice dissolution during wintertime becomes the main cause of the melting alarming level. Over the next 25 years the Arctic ice cap will disappear during summertime. Without the emissions of the greenhouse gases, this situation would had never been possible”… said the research scientist Walt Meier from National Snow and Ice Data Center- NSIDC (USA).
During the last years the glaciers melted exceedingly which led to the formation, in the North Pole area, of a new navigable route between Pacific Ocean and Atlantic Ocean. Otherwise said, from now on there is a “shortcut” between Europe and Asia.
The polar regions are very sensitive to the climatic changes and some science people predict that the glaciers will disappear from the Arctic area until 2040. The analysts plead that the global warming takes place in the Arctic area twice faster than in the other regions of the Planet.
“We have noticed that the glaciers lowered at just 3 million square kilometers”, declared Leif Toudal Pedersen from Danish National Space Center.
The Arctic does not benefit now of an international statute such the Antarctic and it can be asserted and exploited.
In order to preserve the Antarctic, a Treaty was concluded, which determines the international statute of the continent; in 1959 the Treaty was signed by 12 states (Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Chile, France, Japan, New Zealand, Norway, South Africa, Soviet Union, England, United States of America) and it came into force in 1961. Romania signed this Treaty in 1971, being the 17th joining country. Almost 50 countries have now signed the Treaty.
The special thematic philatelic issue follows the initiative launched in 2007 by the presidents of Chile and Finland states. In full agreement the Postal Administrations from these two countries proposed also to other states to join the program of creating a postage stamps issue having as theme preserve the polar regions and glaciers. A series of Northern European countries, but also Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Brazil, South Africa and many other countries joined this project. Romania is one of them.
The stamps issued by the participating countries will have the same specific sign: the graphic symbol of an ice crystal and next to it, the member states of the Antarctic Treaty will also add the outline of the white continent.
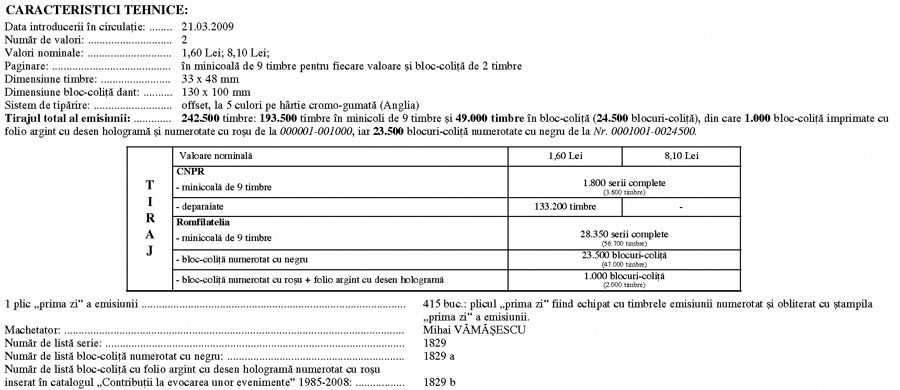
Issue date: 2009-03-21